| |
| |
|
|
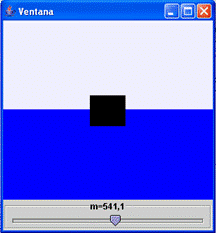
Fig.
7.3: View of the virtual-lab. |
|
|
|
| |
|
| System
description |
| |
This
virtual-lab tries to illustrate the Archimedes' principle: |
| the
buoyant force on a submerged object is equal to the weight of the fluid
displaced. |
| |
The
object is a cube with side equal to 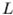 .
In equilibrium, the weight of the submerged object ( .
In equilibrium, the weight of the submerged object (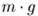 )
is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced ( )
is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced (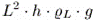 ): ): |
|
where
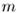 is
the object's mass, is
the object's mass, 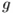 is the gravitational acceleration,
is the gravitational acceleration, 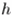 is the submerged height of the cube and
is the submerged height of the cube and 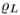 is the fluid density.
is the fluid density. |
| |
| Assuming
that the object is in equilibrium, its submerged height can be calculated
as follows: |
|
| |
| The
virtual-lab allows the user to interactively change the object’s mass.
However, the mass is not allowed to become bigger than: |
|
| If
the mass is bigger, then the object sinks. |
| |
|
|
| Introduction |
| |
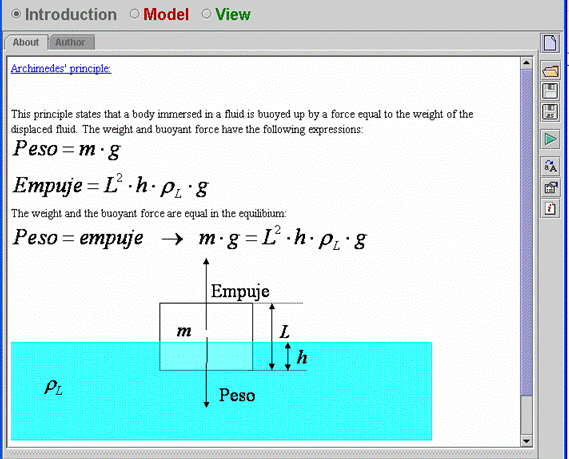
| The
Introduction panel of the virtual-lab is shown in Fig. 7.23. |
| |
|
Fig.
7.23: Introduction. |
|
|
| Model |
| |
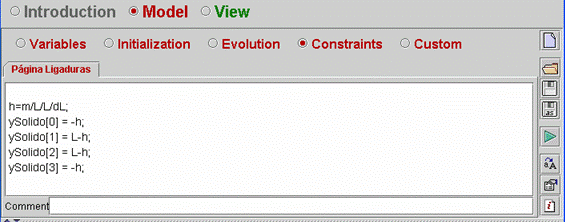
| The
model equation and the array describing the object position are evaluated
in the Constraints panel (see Fig 7.24). Look at the virtual-lab code for
further details. |
| |
|
Fig.
7.24: Constraints panel. |
|
|
| View |
| |
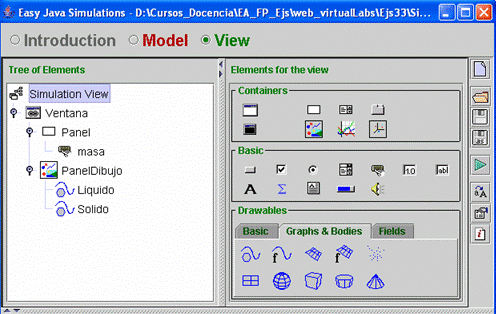
| The
tree of elements is shown in Fig. 7.25. Open the virtual-lab and look at
the properties of the tree elements. |
| |
|
Fig.
7.25: Tree of elements. |
|