 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
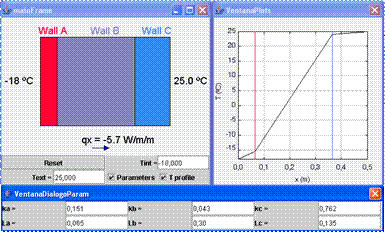
Fig.
7.5: View of the virtual-lab. |
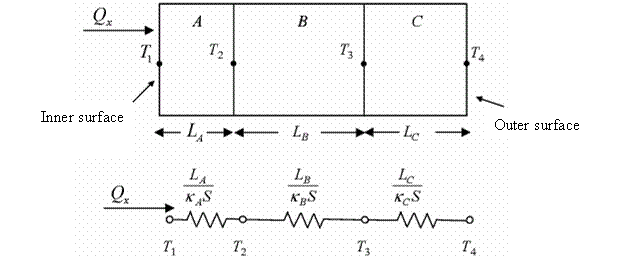
Fig.
7.30: Schematic representation and model of the system.
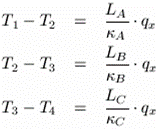
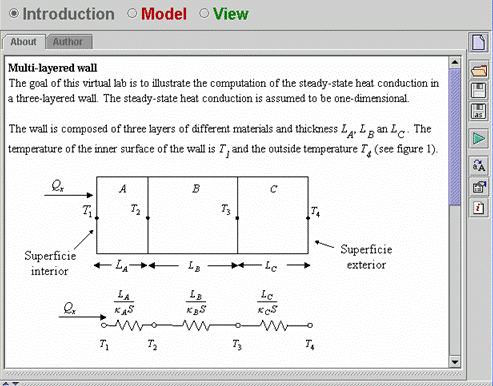
Fig.
7.31: Introduction panel.
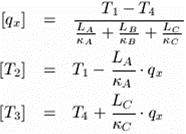
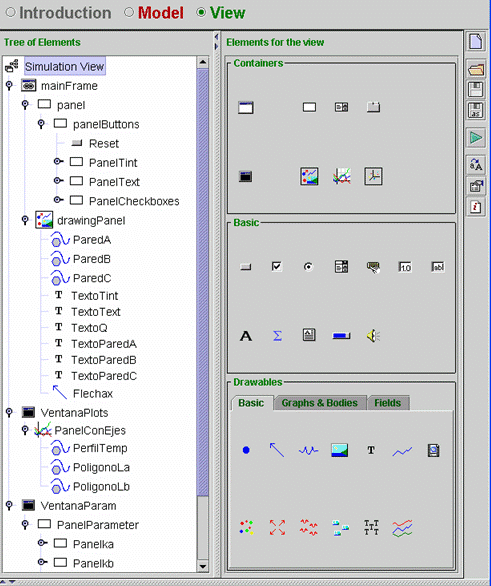
Fig.
7.32: Tree of elements.
7.6
HEAT CONDUCTION IN A THREE-LAYERED WALL |
| << previous | next
>> |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| System description | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| The one-dimensional, steady-state heat flow through a three-layered wall is modeled. The schematic representation of the system and the model (i.e., the series thermal resistors) are shown in Fig. 7.30. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Fig.
7.30: Schematic representation and model of the system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| The mathematical model is composed of the following equations: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
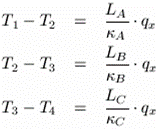 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| The virtual-lab introduction is shown in Fig. 7.31. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Fig.
7.31: Introduction panel. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| The
inner ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
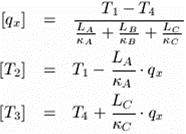 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As the model mimics the steady-state temperature profile for certain boundary conditions, it is static (i.e., time does not play a role in it). Therefore, the model equations are included in the Constraints panel. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| View | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| A part of the tree of elements is shown in Fig. 7.32. Open the virtual-lab and look at the properties of the tree elements. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Fig.
7.32: Tree of elements. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| << previous | next
>> |