 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
Fig.
7.8: View of the virtual-lab. |

Fig.
7.45: Introduction of the virtual-lab.
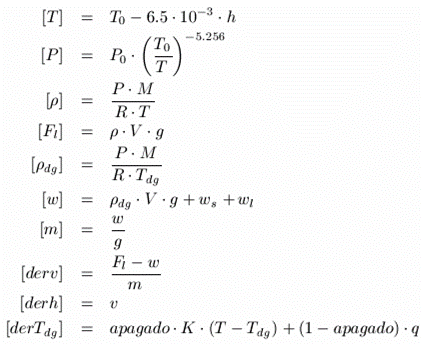
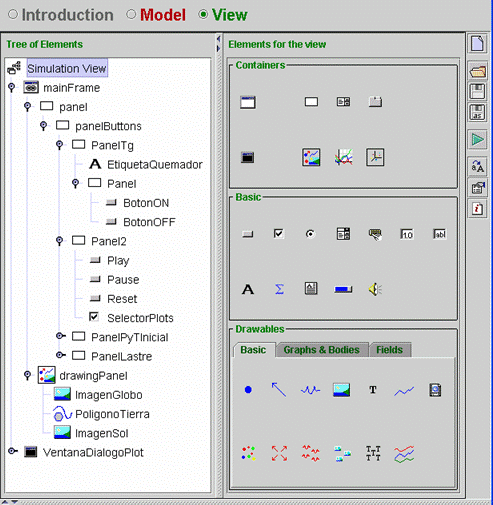
Fig.
7.46: Tree of the elements.
7.9
AEROSTATIC BALLOON |
| << previous | next
>> |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| System description | ||||||||||||||||||||||
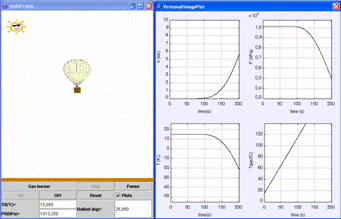
| This virtual lab shows how an aerostatic balloon works. It is a nice example of application of the Archimedes' principle. The buoyant force of the aerostatic baloon is obtained by heating air inside its cavity. The buotant force is due to the difference of density between the hot air inside and the cold air outside the balloon cavity. The buoyant force compensate the balloon weigth (having into account the weight of the ballast and the people). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| The introduction of the virtual-lab is shown in Fig. 7.45. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Fig.
7.45: Introduction of the virtual-lab. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| The model equations sorted and solved, and with the computational causality analyzed, are the following: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
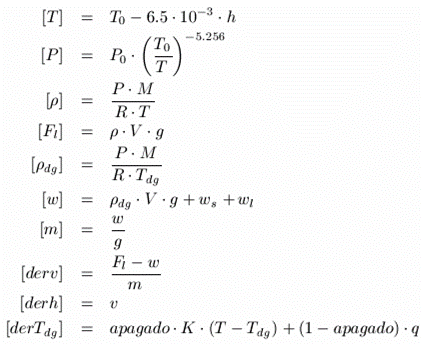 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| View | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| The tree of elements is shown in Fig. 7.46. Open the virtual-lab and look at the properties of the tree elements. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Fig.
7.46: Tree of the elements. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| << previous | next
>> |